The main takeaway: the industry evolved from crisis management to strategic workforce transformation. Big challenges remain, and 2026 will test the resolve of care delivery across the nation, and its willingness to adapt to better support patients and providers alike.
Seven healthcare staffing insights from 2025:
1. The physician shortage reached a critical threshold
The physician shortage intensified this year, with last year’s projections anticipating a deficit of up to 86,000 physicians by 2036. While this has sparked action by legislators, the scale of the crisis shows it must be addressed from other angles as well. Research published in STAT found that residency program limitations stemming from a 1997 Medicare funding cap continue restricting the pipeline.
Rural communities continue to feel the squeeze disproportionately, with nonmetropolitan areas face a projected 58% physician shortage compared to just 5% in urban centers in the coming years.
2. Advanced practice providers filled growing care gaps

Advanced practice continued to gain traction as more states granted full practice authority privileges to these essential providers. Now 30 states and territories have secured enhanced access to advanced practice providers for their patient communities, which includes advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) such as nurse practitioners (NPs), clinical nurse specialists (CNSs), certified nurse midwives (CNMs) and Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs), and also includes physician associates / physician assistants (PAs).
The physician associate profession grew 28% between 2017 and 2021, reaching more than 158,000 certified PAs. Healthcare facilities increasingly relied on APPs in order to maintain care continuity where physician recruitment challenges left gaps in the workforce.
3. Telehealth policy dynamics made effective planning difficult
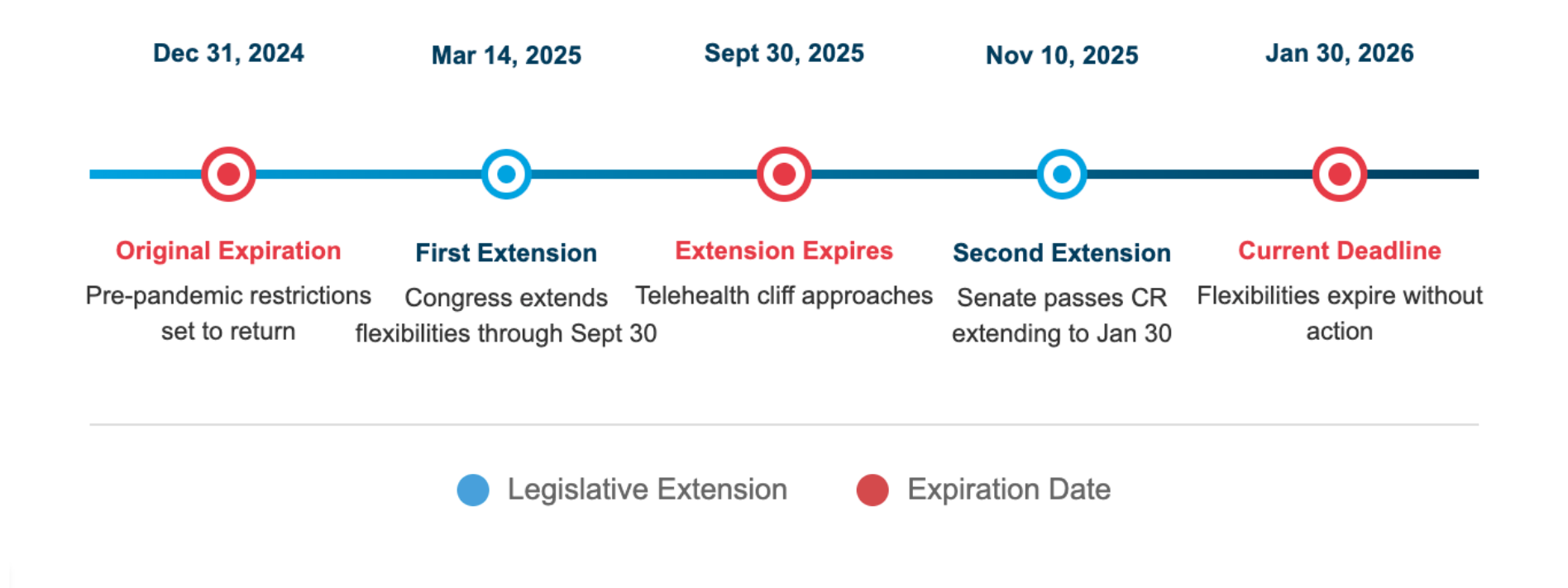
Medicare telehealth flexibilities lapsed during the government shutdown on October 1, 2025, disrupting patient access until services were reinstated weeks later with yet another temporary extension — this time through January 30, 2026. This cycle of bundling telehealth policy with budget continuing resolutions has created persistent uncertainty for systems seeking to make long-term investments in virtual care infrastructure.
Bipartisan legislation offers a potential path forward: the CONNECT for Health Act (S.1261, H.R. 4602) and the Telehealth Modernization Act of 2025 (H.R. 5081) would decouple telehealth from budget negotiations and establish permanent coverage. Until such legislation passes, healthcare organizations must balance the demand for telehealth services against the reality of unpredictable policy timelines.
"This is a dynamic time for telehealth policy, but as a practicing clinician, I've seen firsthand how virtual care improves patient access and outcomes. Our team is actively advocating with legislators for policies that support sustainable telehealth models. We're optimistic policymakers will provide the certainty needed for telehealth to reach its full potential."
- Dr. Jamie Threatt, DNP, AGACNP-BC
Medicare Telehealth Extension Dates, 2024-2026
4. AI implementation accelerated… but in specific use cases
Twenty-two percent of healthcare organizations implemented domain-specific AI tools in 2025, representing a sevenfold increase over 2024. The applications seeing the most traction focused on ambient clinical documentation and back-office revenue cycle management. Research in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association found AI tools for clinical note-taking showed significant promise, though broader diagnostic applications continued facing challenges about data quality and integration.
5. Clinician burnout pushed workforce toward flexibility over compensation
Clinician burnout did not end with the end of the global pandemic. Two in five healthcare workers say that their jobs feel unsustainable, and half say they feel exhausted in their current role. The 2025 Indeed Pulse of Healthcare report reveals that 42% of programs to combat burnout fail to address the root causes. It goes on to cite flexibility and control over schedule among top factors in job satisfaction.
"Healthcare learned the hard way that throwing money at retention doesn’t guarantee success, and competitive pay doesn’t fix burnout. Physicians and NPs are seeking control of their schedules and a sense of meaning in their work."
— Amelia Vietri, senior vice president, surgery, hospital and clinic-based and internal medicine sub-specialties, LocumTenens.com
6. Rural healthcare access became a workforce imperative
The rural-urban divide widened significantly. In 2024, rural areas struggled to keep up with metropolitan regions in some areas. This year the National Rural Health Association highlighted how physician burnout in rural settings, due to higher on-call demands and limited backup, ramped up the need for sustainable solutions.
7. Cost pressures forced innovation in staffing models
Healthcare facilities made an intentional shift toward hybrid models to adjust to increasing operational costs. Staffing Industry Analysts projected healthcare staffing revenues would decline 6% in 2025 to approximately $39.4 billion, reflecting both market correction and efficiency gains from optimized workforce planning.
Looking ahead to 2026

Telehealth permanence is top of mind.
- Telehealth is a growing segment of the healthcare market, and what shape it takes depends on upcoming congressional action.
January 2026 could see dramatic changes in virtual care access, especially for rural and underserved populations. - Organizations should monitor legislative developments and prepare contingency plans. Hybrid telehealth models that combine virtual and in-person care may prove most resilient.
Physician-APP team models will continue to evolve.
- As the tug-of-war regarding scope of practice persists, successful organizations will optimize team-based care delivery rather than focus on niche credential distinctions. Collaborative care models maximize care delivery and balance responsibilities in a team-based approach.
- Strategic utilization of APP workforces can extend clinic hours, improve access and reduce physician burnout when implemented thoughtfully with stakeholders.
AI implementation will shift from proof of concept to ROI demonstration.
- Time is up for the brainstorming phase of AI. Going forward, healthcare leaders will demand measurable outcomes like reduced documentation time, improved scheduling efficiency or enhanced clinical decision support.
- Tools lacking clear value propositions will face increased scrutiny as organizations tighten technology budgets and seek to increase efficiency across the spectrum of operations.
Workforce sustainability requires cultural transformation.
- Flexible staffing, improved work-life balance and reduced administrative burden are no longer optional.
- Organizations that fail to address root causes of burnout will continue facing costly turnover regardless of compensation. Flexible staffing models that give clinicians control over their schedules are becoming the baseline expectation.
Incorporation of managed services into healthcare strategy will grow.
- The adoption and implementation of managed services will accelerate in 2026. Healthcare is the fastest-growing vertical for VMS adoption with a CAGR of 13.7% through 2033, overtaking the overall market growth.
- More specifically, the contingent workforce VMS market specifically will reach $20 billion by 2033 as healthcare organizations seek to replace administrative overhead with greater efficiency.
- Workforce optimization solutions offering vendor accountability and which provide visibility into multi-location staffing, vendor management and data-driven decision-making will become essential infrastructure for success.
Providing the best care in 2026
Success in 2026 requires unprecedented agility in workforce planning. The convergence of persistent shortages, potential policy pivots and evolving care delivery models demands proven partnerships that can provide both immediate coverage and strategic workforce solutions.